Understanding the Importance of Boat Sealants and Protective Coatings
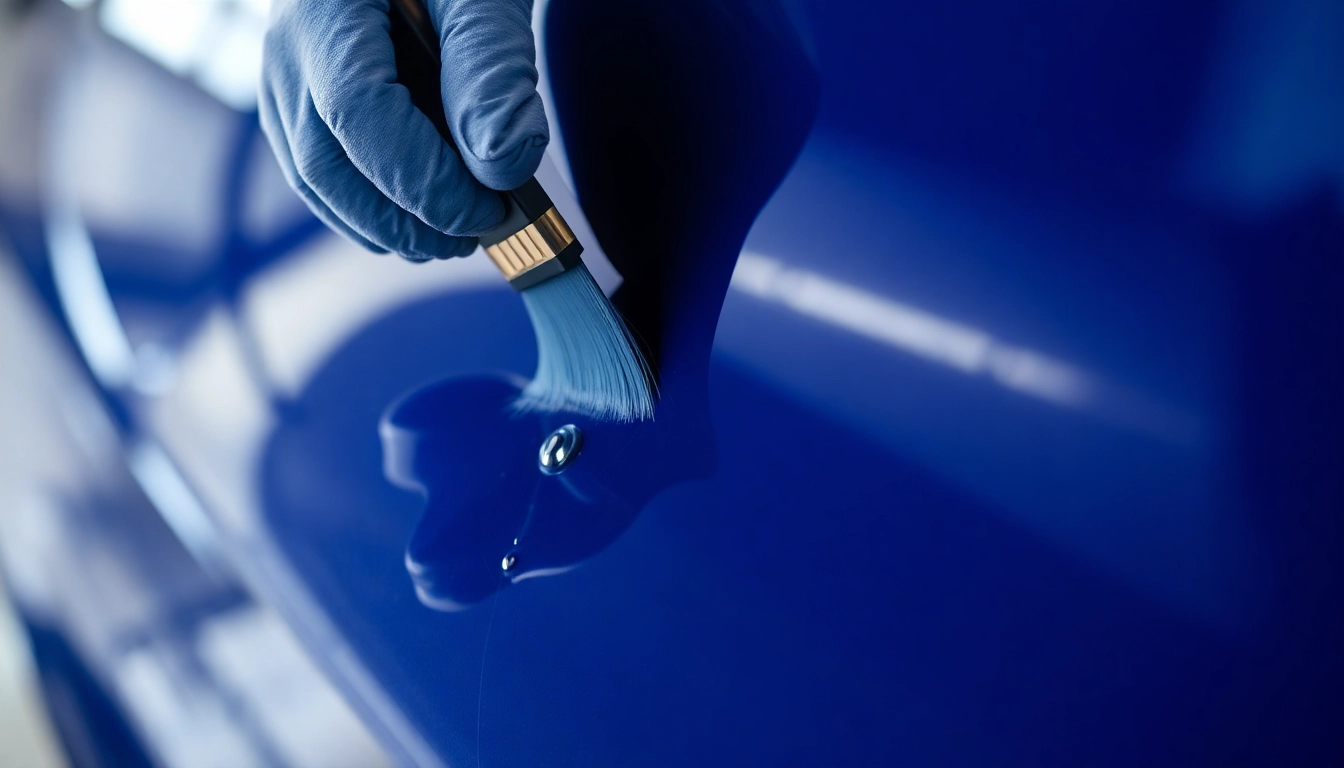
Proper maintenance and protection of your watercraft are paramount to ensuring longevity, optimal performance, and aesthetic appeal. Among the essential products in any boat owner’s toolkit are Boots Versiegelung—a specialized sealing solution designed to shield gelcoat and painted surfaces from environmental stresses. Unlike regular waxes, which provide superficial gloss and limited durability, high-quality sealants create a robust barrier against UV rays, saltwater, pollutants, and mechanical wear, significantly extending the lifespan of your vessel’s exterior.
Today, the market offers a variety of marine-grade sealants, each tailored to specific surface types and operational conditions. Selecting the right product is crucial for achieving long-lasting protection, maintaining vessel value, and ensuring ease of maintenance. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the advantages of boat sealants, how they compare to traditional waxing, and what you need to consider when choosing and applying the perfect coating for your boat.
Advantages of Marine-Grade Boots Sealants
Enhanced Durability and Environmental Resistance
Marine sealants form a durable polymer film that adheres tightly to gelcoat surfaces, providing excellent resistance against harsh environmental factors. This includes protection from UV-induced degradation, oxidation, and chemical corrosion caused by saltwater and pollutants. Studies have shown that properly applied sealants can extend the life of gelcoat by up to 50%, reducing the need for expensive repairs or re-fairing.
Superior Gloss and Surface Smoothness
In addition to protecting, a high-quality sealant enhances the boat’s appearance by delivering a deep, glossy finish that optimizes hydrodynamics. A smooth surface reduces water friction, which can lead to improved fuel efficiency and faster speeds. This is particularly valuable for racing boats or vessels operating in competitive environments.
Ease of Maintenance and Cleaning
Sealants make cleaning the vessel simpler by creating a hydrophobic effect—dirt, grime, and water bead off the surface effortlessly. This not only preserves the aesthetic but also minimizes abrasive cleaning efforts, saving time and labor costs during regular maintenance.
Distinguishing Sealants from Waxes and Other Coatings
Sealants vs. Waxes
While traditional waxes have been favored for their ease of use and natural shine, they generally provide only short-term protection—lasting a few weeks to a couple of months. Waxes penetrate the gelcoat’s surface temporarily, and are susceptible to washing out with frequent water exposure or cleaning.
Contrarily, modern polymer and ceramic sealants bond chemically with the gelcoat, forming a resilient, long-lasting shield that can endure several months to over a year with proper maintenance. Furthermore, while waxes tend to diminish the gloss over time, sealants maintain a more consistent appearance due to their durable film.
Other Protective Coatings
Ceramic coatings, a subset of advanced sealants, incorporate nanotechnology to create an even harder surface with unparalleled resistance to scratches, contaminants, and UV damage. These coatings often require professional application but deliver results that can last multiple years, making them ideal for owners seeking premium protection.
Key Properties for Effective Marine Sealants
Choosing the appropriate sealant involves understanding its material composition and application suitability. Essential properties include:
- Hydrophobicity: Repels water to prevent salt and dirt accumulation.
- UV Resistance: Protects gelcoat from sun-induced oxidation.
- Adhesion Strength: Bonds effectively to gelcoat and painted surfaces.
- Ease of Application: Allows smooth, even coverage without streaks or bubbles.
- Durability: Maintains protective qualities over extended periods with minimal reapplication.
Products like the Power Sealer and Gelcoat Premium Protection have been formulated with these attributes, employing advanced polymer and nanotech formulations to maximize performance.
Selecting the Right Sealant: What to Consider
Surface Material Compatibility
Marine surfaces vary from gelcoat to painted finishes, fiberglass, and metal trims. Ensuring the sealant’s compatibility prevents issues such as peeling or staining. Most marine sealants specify suitable surfaces—consult manufacturer instructions for optimum results.
Environmental and Water Conditions
Vessels operating in saltwater require highly resistant, hydrophobic coatings to withstand corrosive elements. Freshwater boats might opt for less aggressive formulations but still benefit from UV and dirt resistance. Consider climate factors—high UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, and pollution levels influence sealant choice.
Application Methodology for Best Results
Proper application techniques—cleaning, surface preparation, and curing—are vital. Using tools like foam applicators, polishing pads, or even specialized sprayers (e.g., the FoamMaster FM 10) can enhance uniform coverage. Adhering to curing times and avoiding exposure to water during initial set-up is crucial for lasting protection.
Applying Marine Sealants: Step-by-Step Guide
Preparation and Surface Cleaning
Start by thoroughly cleaning the surface with a high-quality, pH-neutral cleaner like the Duo Power Clean Set. Remove any existing wax, dirt, or oxidation with a dedicated polish or cleaner to ensure optimal adhesion. Use microfibre towels and soft brushes to prevent scratches.
Application Process
Apply the sealant evenly with a foam or microfiber applicator, working in small sections. For best results, work in a shaded area, maintaining a consistent application pressure. Some products, such as Power Polish, can assist in preparing the surface for sealing. After initial application, buff the surface with an orange or Waffelpad for a high-gloss finish.
Drying and Curing
Allow the sealer to cure according to manufacturer instructions—typically 24-48 hours—without exposing the boat to water or harsh weather. This ensures the polymer bonds are fully developed, providing maximum protection.
Maintenance and Longevity of Sealed Surfaces
Routine Cleaning Tips
Maintain the sealant’s effectiveness by rinsing the vessel with fresh water after use and cleaning with gentle, pH-neutral products. Avoid abrasive cleaners or brushes which can degrade the protective film.
Refreshing the Sealant
Over time, the protective layer can diminish, especially in high UV or saltwater environments. Reapplying a compatible sealant—often in the form of a quick spray or wipe-on coating—restores the shield and gloss. Regular application intervals depend on usage, typically every 6-12 months.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Applying sealants on dirty or contaminated surfaces, neglecting proper curing times, or using incompatible products can lead to uneven coverage, reduced protection, and costly repairs. Always adhere to manufacturer guidelines and perform patch tests if unsure.
Comparing Sealants with Other Protective Methods
Polymer and Ceramic Coatings: The Benefits
Compared to traditional waxing, polymer and ceramic coatings deliver superior longevity, chemical resistance, and surface hardness. For instance, the Power Sealer employs advanced polymer technology to create a semi-permanent barrier that withstands multiple seasons.
Long-Term Performance and Maintenance
Ceramic coatings can last several years, reducing the frequency of reapplication and overall maintenance costs. They also provide enhanced shine and protection against minor scratches, making them ideal for frequent watercraft users or commercial vessels.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
While initial investment in high-end sealants or coatings may be higher, the long-term savings in repair, polishing, and re-coating expenses justify the expense. A professional application ensures optimal results, but DIY options are also effective when following proper procedures and using quality products.